
Dim3 grid cuda full#
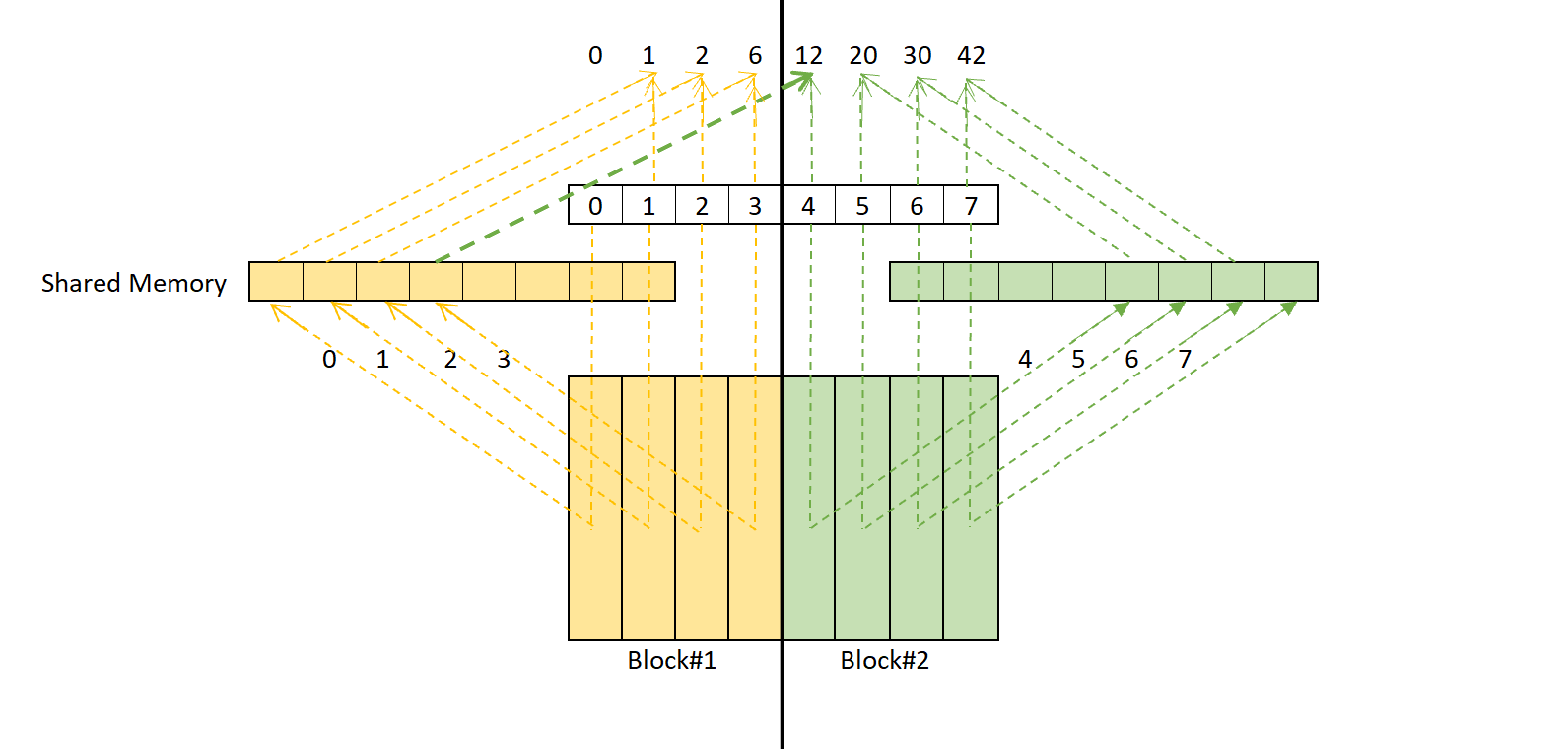
number of threads in a block in the x dimension) Full global thread ID in x dimension can be computed by: x = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x Įxample - x direction A 1-D grid and 1-D block 4 blocks, each having 8 threads Global ID 26 threadIdx.x threadIdx.x threadIdx.x threadIdx.x 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 blockIdx.x = 0 blockIdx.x = 1 blockIdx.x = 2 blockIdx.x = 3 gridDim = 4 x 1 blockDim = 8 x 1 Global thread ID = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x = 3 * = thread 26 with linear global addressing Derived from Jason Sanders, "Introduction to CUDA C" GPU technology conference, Sept. ThreadIdx.x - “thread index” within block in “x” dimension blockIdx.x - “block index” within grid in “x” dimension blockDim.x - “block dimension” in “x” dimension (i.e. The first argument in the execution configuration specifies the number of thread blocks in the grid, and the second specifies the number of. In the CUDA programming model we speak of launching a kernel with a grid of thread blocks.
Dim3 grid cuda software#
If want a 1-D structure, can use a integer for B and T in: myKernel>(arg1, … ) B – An integer would define a 1D grid of that size T –An integer would define a 1D block of that size Example myKernel>(arg1, … ) ħ CUDA Built-in Variables for a 1-D grid and 1-D block In CUDA there is a hierarchy of threads in software which mimics how thread processors are grouped on the GPU. T – a structure that defines the number of threads in a block in each dimension (1D, 2D, or 3D). These variables are of type dim3, a CUDA built-in integer. Compute capability 1.0 Maximum number of threads per block = 512 Maximum sizes of x- and y- dimension of thread block = 512 Maximum size of each dimension of grid of thread blocks = 65535ĭefining Grid/Block Structure Need to provide each kernel call with values for two key structures: Number of blocks in each dimension Threads per block in each dimension myKernel>(arg1, … ) B – a structure that defines the number of blocks in grid in each dimension (1D or 2D). blockDim (block dimension, measured in threads) and gridDim (grid dimension, measured in blocks). NVIDIA defines “compute capabilities”, 1.0, 1.1, … with these limits and features supported. Can be 1 or 2 dimensions Can be 1, 2 or 3 dimensions CUDA C programming guide, v 3.2, 2010, NVIDIAĤ Device characteristics - some limitations Linked to internal organization Threads in one block execute together. NVIDIA GPUs consist of an array of execution cores each of which can support a large number of threads, many more than the number of cores Threads grouped into “blocks” Blocks can be 1, 2, or 3 dimensional Each kernel call uses a “grid” of blocks Grids can be 1 or 2 dimensional Programmer will specify the grid/block organization on each kernel call, within limits set by the GPUĪllows flexibility and efficiency in processing 1D, 2-D, and 3-D data on GPU.
These notes will introduce: One dimensional and multidimensional grids and blocks How the grid and block structures are defined in CUDA Predefined CUDA variables Adding vectors using one-dimensional structures Adding/multiplying arrays using 2-dimensional structures ITCS 6/8010 CUDA Programming, UNC-Charlotte, B.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
